Csf produced and or flowing into the fourth ventricle can exit to the subarachnoid space through lateral apertures and a single median aperture located in the inferiorportion of the roof.
Fourth ventricle roof and floor.
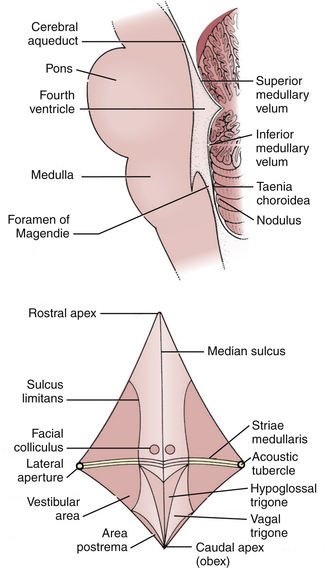
The caudal tip of the fourth ventricle where it becomes the central canal is known as the obex.
On every side the 4th ventricle is limted inferiolaterally by the inferior cerebellar peduncle sup plemented by gracile and cuneate tubercles and superolaterally by the superior cerebellar peduncle.
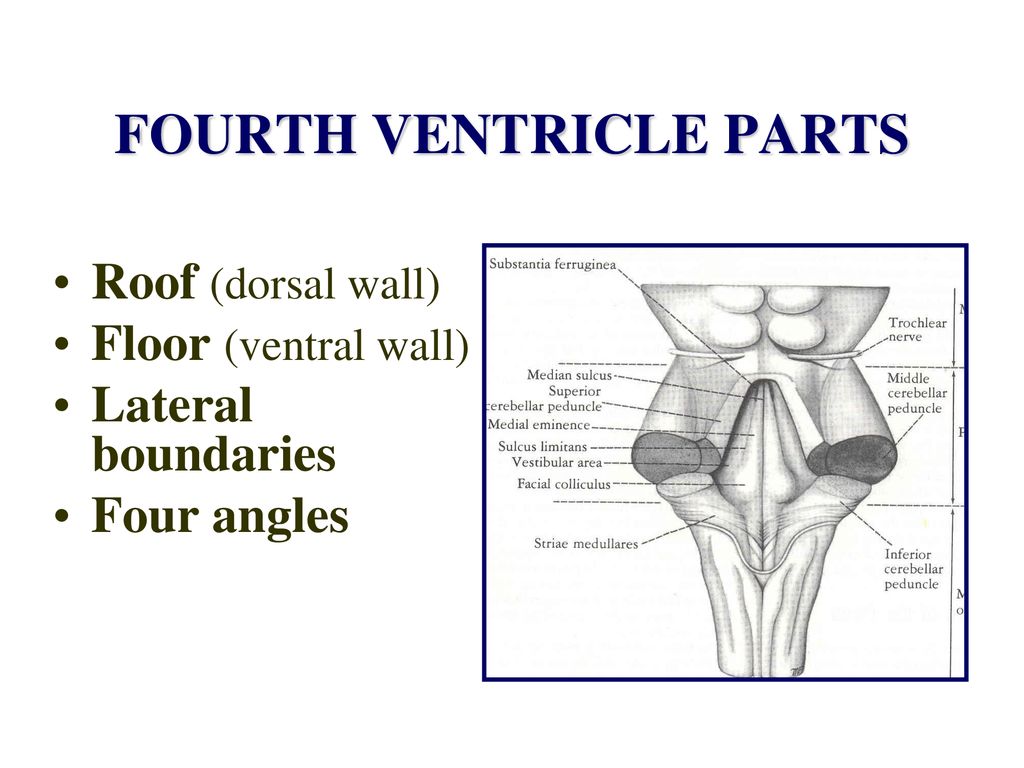
The bounds of the 4th ventricle contain sidelong boundaries a roof and a floor lateral bounds lateral walls.
Roof of the fourth ventricle formed by thin laminae of white matter.
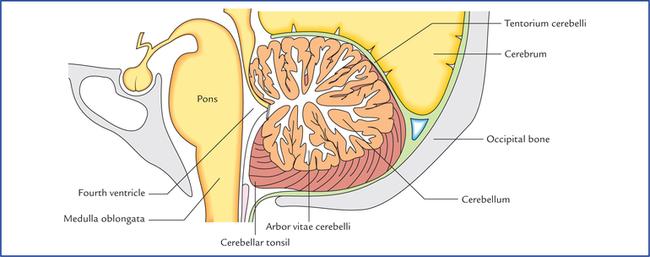
The fourth ventricle has an anterior ventral floor with a characteristic diamond shape named the rhomboid fossa and a posterior dorsal tent shaped roof.
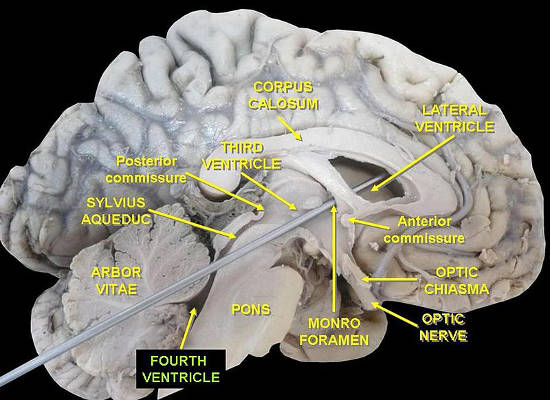
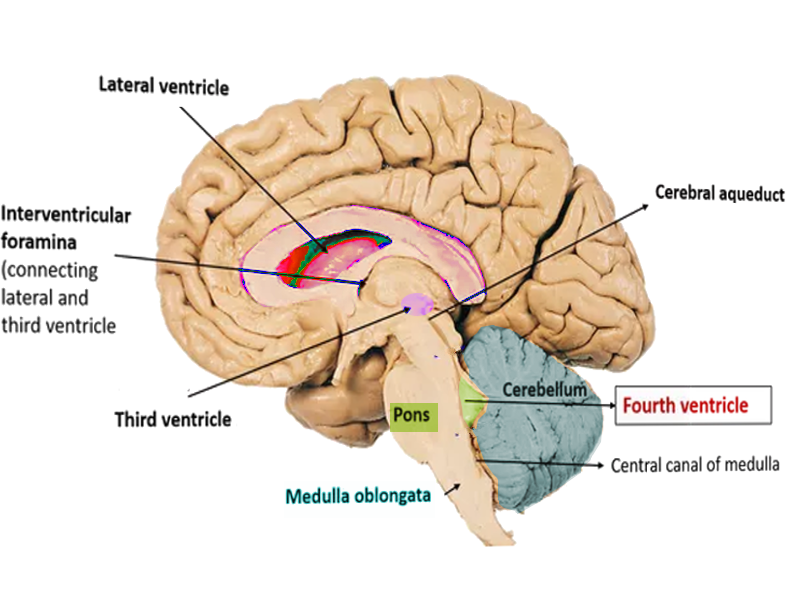
The fourth ventricle contains cerebrospinal fluid.
The roof is composed of the cerebellum.
This ventricle has a roof and a floor.
The posterior boundary or roof of the fourth ventricle is very thin and concealed by the cerebellum.
This region contains the cardiorespiratory deglutition and vasomotor centers.
The fourth ventricle has lateral boundaries a roof and a floor.
The lowermost portion of the floor of the fourth ventricle is called the calamus scriptorius as it appears to resemble the tip of a pen.
The fourth ventricle has a roof at its upper posterior surface and a floor at its lower anterior surface and side walls formed by the cerebellar peduncles nerve bundles joining the structure on the posterior side of the ventricle to the structures on the anterior side.